Bệnh tiểu đường (đái tháo đường) là một trong những bệnh mạn tính phổ biến nhất trên toàn cầu, ảnh hưởng đến hàng trăm triệu người. Hầu hết mọi người đều biết đến các biến chứng thường gặp như bệnh tim mạch, đột quỵ, mờ mắt, bệnh thận hay nguy cơ cắt cụt chi dưới. Tuy nhiên, vẫn còn một biến chứng ít được chú ý nhưng gây ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến chất lượng sống — teo cơ do đái tháo đường.
Điểm đặc biệt của biến chứng này là nó chỉ chiếm khoảng 1% ở người trưởng thành mắc bệnh tiểu đường, và cơ chế tác động khác so với những dạng tổn thương thần kinh khác. Việc nhận biết sớm triệu chứng, hiểu rõ nguyên nhân, đồng thời theo dõi chỉ số đường huyết thường xuyên bằng máy đo đường huyết hoặc máy thử đường sẽ đóng vai trò quan trọng giúp giảm nguy cơ tiến triển bệnh.

Teo cơ do đái tháo đường, còn được gọi bằng các tên chuyên môn như:
Khác với dạng bệnh thần kinh ngoại biên thường ảnh hưởng đến bàn chân và cẳng chân, teo cơ do đái tháo đường gây tổn thương chủ yếu ở các dây thần kinh vùng đùi, hông, mông, và đôi khi lan lên ngực hoặc bụng. Bệnh thường khởi phát đột ngột hoặc bán cấp, tiến triển qua nhiều giai đoạn, từ một bên cơ thể rồi dần lan sang hai bên.
Nguyên nhân cốt lõi của hầu hết các biến chứng bệnh tiểu đường, bao gồm teo cơ, đều bắt nguồn từ tình trạng tăng đường huyết kéo dài hoặc biến động quá nhanh. Chính vì vậy, theo dõi chỉ số đường huyết đều đặn là biện pháp phòng ngừa quan trọng.
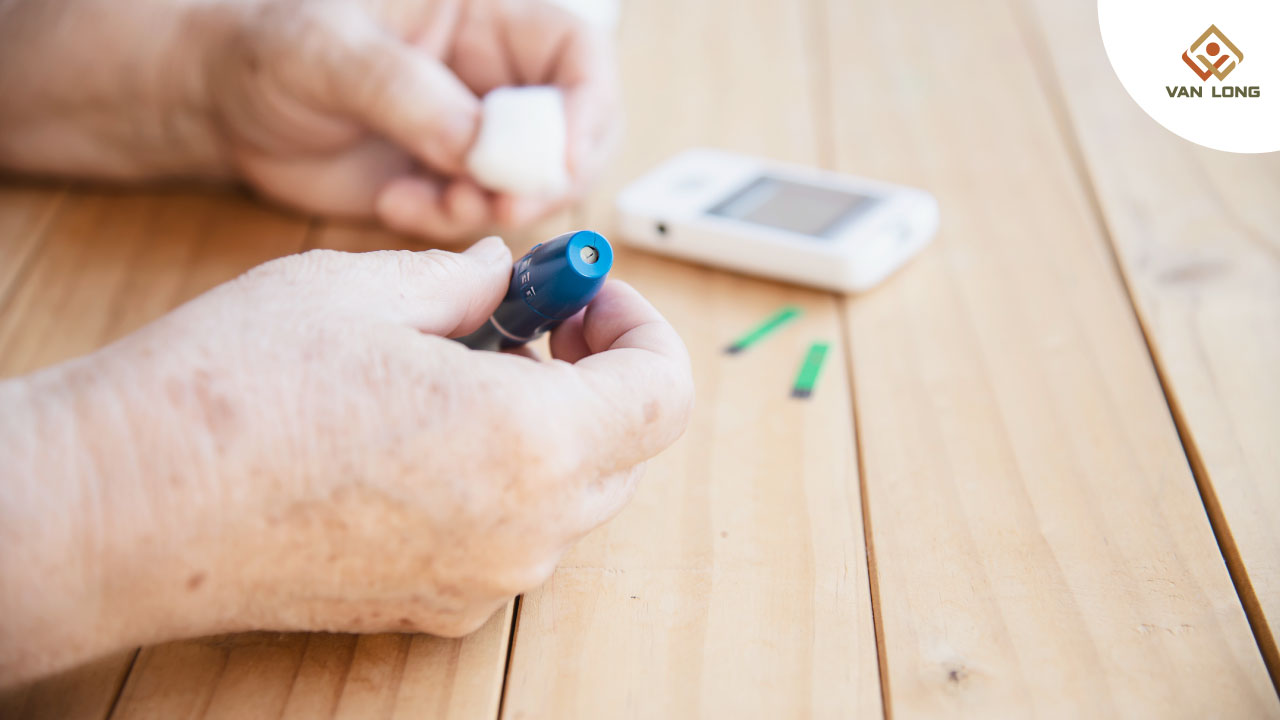
Các thiết bị máy đo đường huyết hoặc máy thử đường hiện nay cho phép người bệnh đo máu tại nhà, giúp phát hiện sớm các bất thường, điều chỉnh chế độ ăn, tập luyện và thuốc kịp thời. Việc này không chỉ giúp ngăn ngừa biến chứng mạch máu mà còn giảm nguy cơ mắc các dạng tổn thương thần kinh hiếm gặp như teo cơ.

Bệnh thường gặp ở người cao tuổi, trung bình khoảng 65 tuổi, nhưng không loại trừ người trẻ hơn. Các triệu chứng đặc trưng:
Bệnh có thể kéo dài từ vài tháng đến 2 năm, sau đó ổn định và hồi phục một phần. Tuy nhiên, nếu không quản lý chỉ số đường huyết tốt, nguy cơ tái phát hoặc để lại di chứng yếu cơ là khá cao.
Hiện tại, cơ chế chính xác gây teo cơ do đái tháo đường vẫn chưa được xác định. Một số nghiên cứu cho rằng viêm vi mạch qua trung gian miễn dịch đóng vai trò quan trọng.
Nguy cơ cao hơn ở các đối tượng:
Các yếu tố kích hoạt có thể gồm:

Nếu không được điều trị kịp thời, teo cơ do đái tháo đường có thể dẫn tới:
Điều này cho thấy việc đo máu tại nhà và theo dõi sức khỏe định kỳ giúp phát hiện sớm biến chứng, tránh những can thiệp y tế không cần thiết.
Người bệnh cần đến bác sĩ ngay nếu:
Những triệu chứng này đặc biệt đáng chú ý ở bệnh nhân bệnh tiểu đường mới được chẩn đoán hoặc có chỉ số đường huyết biến động bất thường.
Bác sĩ sẽ loại trừ các bệnh khác như thoái hóa cột sống, nhồi máu cơ do tiểu đường, hội chứng Meralgia paresthetica. Các xét nghiệm bao gồm:
Việc chẩn đoán sớm giúp xây dựng kế hoạch điều trị phù hợp, tránh biến chứng lâu dài.
Hiện chưa có phương pháp điều trị đặc hiệu, nhưng đa phần bệnh sẽ cải thiện theo thời gian nếu được quản lý tốt.
Các hướng điều trị chính:

Việc kiểm soát khẩu phần ăn giúp giữ chỉ số đường huyết ổn định, hỗ trợ điều trị và ngăn biến chứng.

Teo cơ do đái tháo đường tuy hiếm gặp nhưng ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến chất lượng sống. Việc nhận biết sớm triệu chứng, kết hợp với quản lý chỉ số đường huyết chặt chẽ, là chìa khóa phòng ngừa và điều trị hiệu quả.
Ngày nay, với sự hỗ trợ của máy đo đường huyết và máy thử đường, người bệnh có thể chủ động đo máu tại nhà, từ đó điều chỉnh chế độ ăn uống, tập luyện và thuốc một cách khoa học. Điều này không chỉ giúp phòng ngừa teo cơ mà còn giảm nguy cơ nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm khác của bệnh tiểu đường.
——————————
CÔNG TY TNHH PHÁT TRIỂN THƯƠNG MẠI DỊCH VỤ VÂN LONG
YOUR NEEDS - OUR BUSINESS
Hotline: (028) 3526 2468 / 098.484.0440
Email: cskh@vl-groups.com
Website: www.vl-groups.com
Địa chỉ:
- Văn phòng HCM: Tòa nhà Fosco, D35 + D36 - 40 Bà Huyện Thanh Quan, P.Xuân Hòa, TP. HCM
- Trung tâm bảo hành: 373/14 Nguyễn Kiệm, P.Đức Nhuận, TP.HCM
- Văn phòng Hà Nội: Khu VP Hồng Hà, 38.3/1 Ngõ 109 Trường Chinh, P.Phương Liệt, Q.Thanh Xuân, Hà Nội
- Kho Tổng: 938 Quốc Lộ 1A, P.Linh Xuân, TP.HCM
🌼 Shopee: https://shopee.vn/vanlonggroups
🌼 Tiktok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thietbichamsocsuckhoe
🌼 Tiki: https://tiki.vn/cua-hang/cham-soc-suc-khoe-van-long
🌼 Lazada: https://www.lazada.vn/shop/van-long-our-needs-your-business