Khó thở, hay còn gọi là hụt hơi, không chỉ là cảm giác thiếu không khí mà còn là một tín hiệu cảnh báo cơ thể đang gặp vấn đề nghiêm trọng về sức khỏe. Theo một nghiên cứu tại Đức năm 2016, cứ 4 bệnh nhân đến khoa cấp cứu thì có 1 người bị khó thở. Đây là triệu chứng phổ biến nhưng tiềm ẩn nhiều nguy cơ, đặc biệt khi nguyên nhân xuất phát từ tim hoặc phổi.
Bài viết này sẽ phân tích toàn diện từ khái niệm, nguyên nhân, triệu chứng, biến chứng, cho đến phương pháp chẩn đoán, điều trị và phòng ngừa khó thở. Đồng thời, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu máy tạo oxy đóng vai trò thế nào trong hỗ trợ hô hấp, cũng như khi nào cần dùng máy tạo oxy dựa trên chỉ định y khoa.
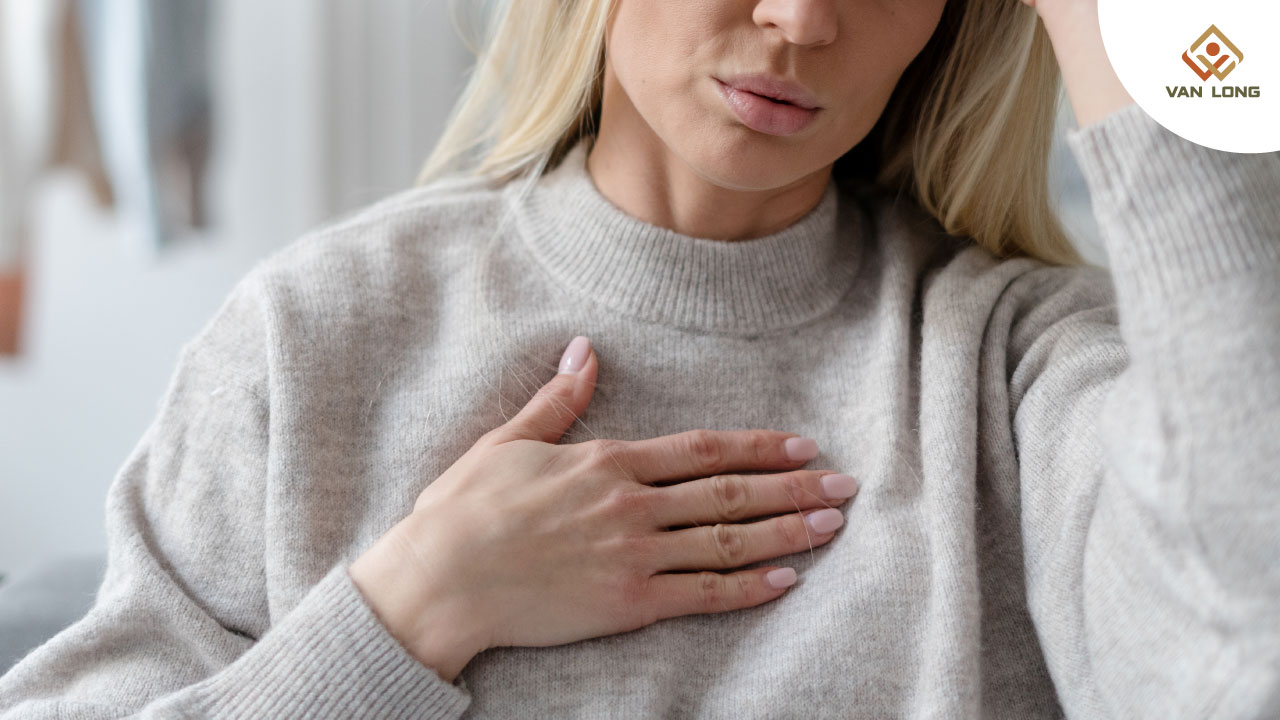

Khó thở (Dyspnea) là cảm giác chủ quan của người bệnh về việc hít thở khó khăn, không thoải mái, hoặc phải gắng sức nhiều để hít thở. Một số mô tả tình trạng này như “thở nông”, “hụt hơi” hay “ngạt thở”.
Đặc điểm:
Phân loại:
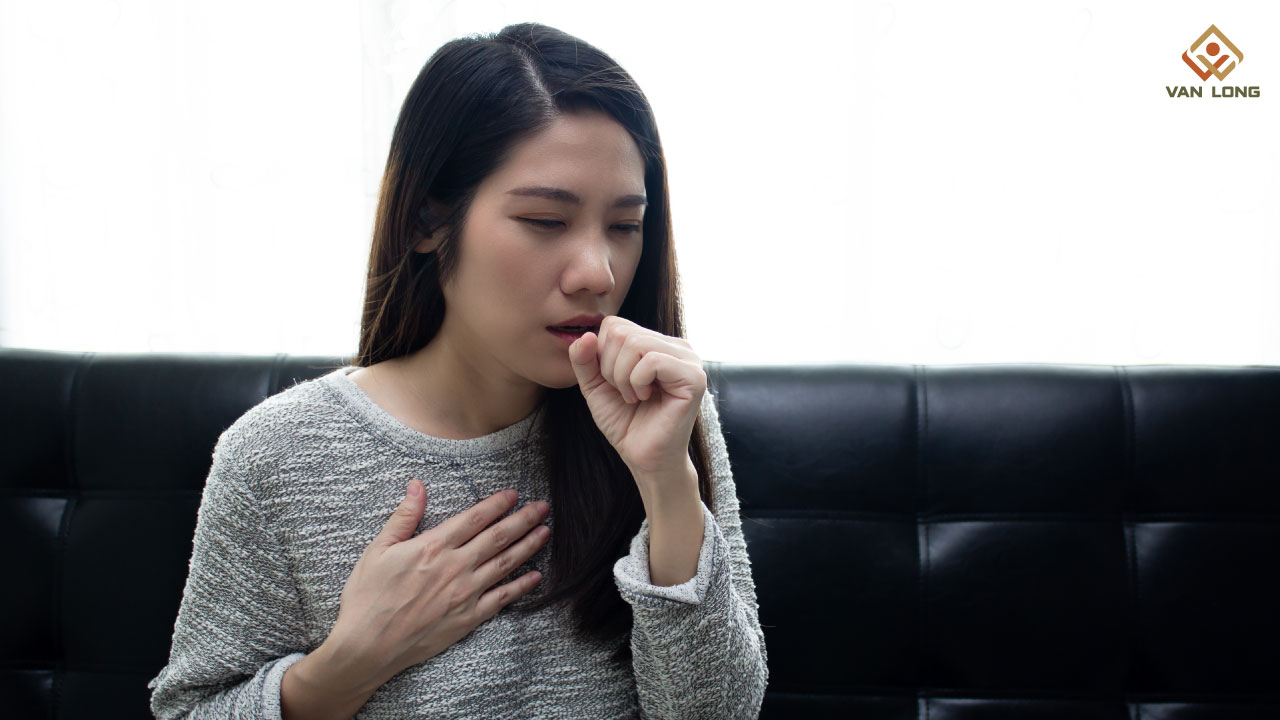

Khó thở không chỉ đơn thuần là thiếu oxy mà còn kéo theo một loạt dấu hiệu khác. Tùy nguyên nhân, bệnh nhân có thể gặp:
Những biểu hiện này đặc biệt đáng lo khi xuất hiện cùng lúc, vì có thể báo hiệu tình trạng suy hô hấp cần hệ thống khí oxy và thiết bị hỗ trợ ngay lập tức.
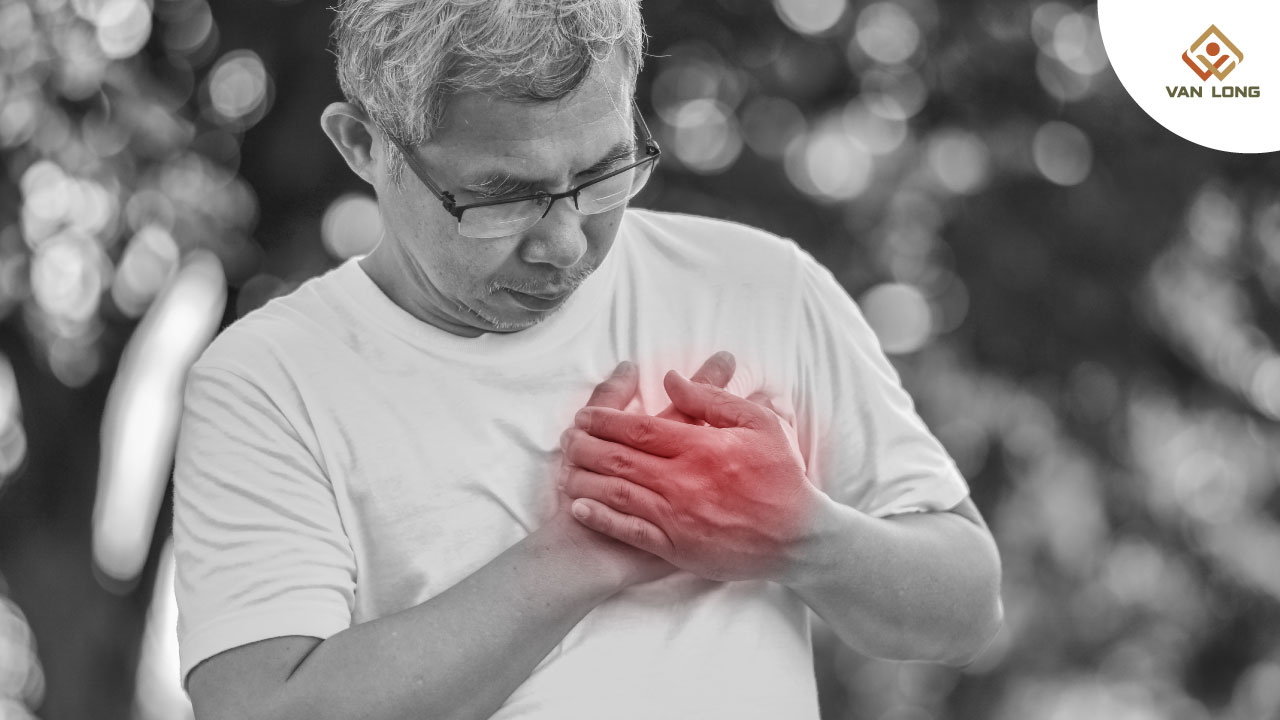

Khó thở kéo dài hoặc xuất hiện đột ngột mà không được xử trí đúng cách có thể dẫn đến:
Trong nhiều trường hợp, can thiệp bằng máy tạo oxy hoặc các thiết bị y tế chuyên dụng là yếu tố sống còn.
Bạn nên đến cơ sở y tế ngay nếu:
Những tình huống này yêu cầu hồi sức cấp cứu khẩn cấp và có thể cần thở oxy ngay tại hiện trường.
Nhiều nguyên nhân trong số này khiến nồng độ oxy máu giảm lâu dài, buộc bệnh nhân phải dùng máy tạo oxy tại nhà.
Bác sĩ sẽ:
Dựa vào kết quả, bác sĩ sẽ quyết định khi nào cần dùng máy tạo oxy hoặc các biện pháp khác.
Hệ thống khí oxy tại bệnh viện bao gồm:
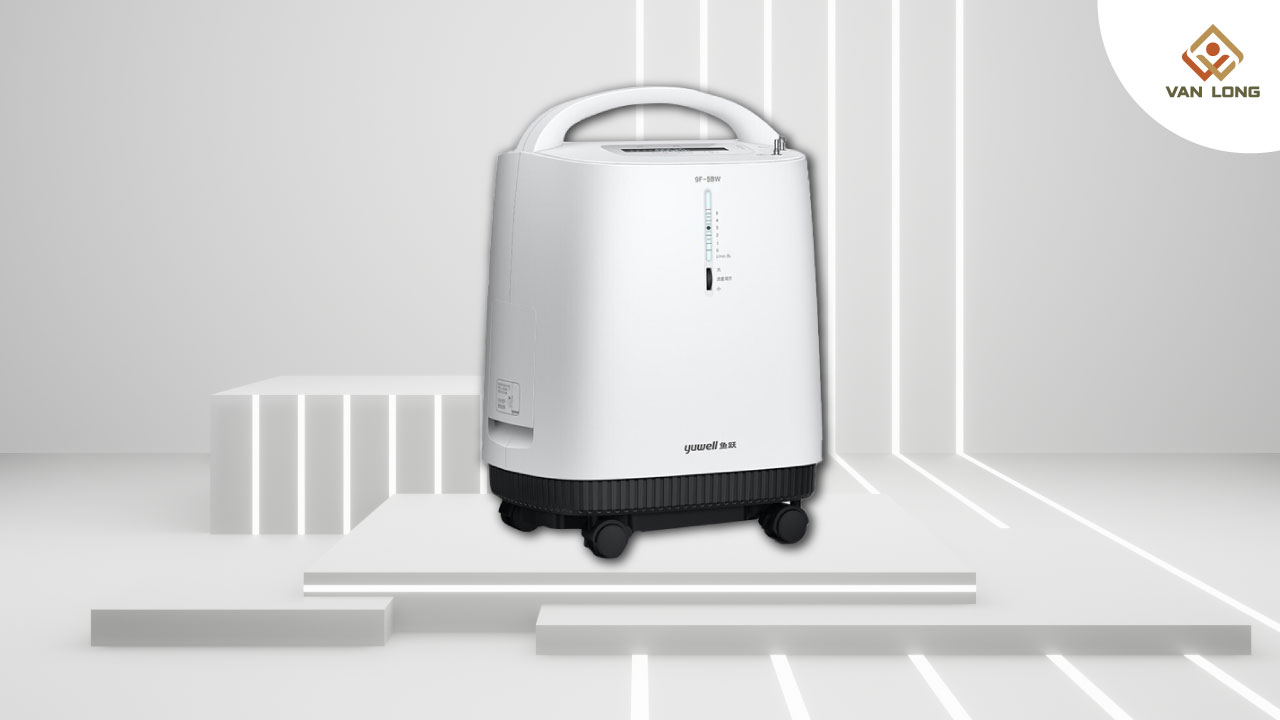

Máy tạo oxy là thiết bị y tế giúp tách oxy tinh khiết từ không khí. Ưu điểm:
Khi nào cần dùng máy tạo oxy?
Việc dùng máy phải theo chỉ định của bác sĩ, tránh tự ý sử dụng.

Khó thở là triệu chứng cần được quan tâm nghiêm túc. Việc hiểu rõ nguyên nhân, dấu hiệu nguy hiểm và khi nào cần dùng máy tạo oxy sẽ giúp bệnh nhân chủ động bảo vệ sức khỏe.
Máy tạo oxy không chỉ hỗ trợ hô hấp tại nhà mà còn là giải pháp quan trọng trong điều trị lâu dài cho nhiều bệnh nhân hô hấp mạn tính, khi được sử dụng đúng chỉ định và kết hợp lối sống lành mạnh.
——————————
CÔNG TY TNHH PHÁT TRIỂN THƯƠNG MẠI DỊCH VỤ VÂN LONG
YOUR NEEDS - OUR BUSINESS
Hotline: (028) 3526 2468 / 098.484.0440
Email: cskh@vl-groups.com
Website: www.vl-groups.com
Địa chỉ:
- Văn phòng HCM: Tòa nhà Fosco, D35 + D36 - 40 Bà Huyện Thanh Quan, P.Xuân Hòa, TP. HCM
- Trung tâm bảo hành: 373/14 Nguyễn Kiệm, P.Đức Nhuận, TP.HCM
- Văn phòng Hà Nội: Khu VP Hồng Hà, 38.3/1 Ngõ 109 Trường Chinh, P.Phương Liệt, Q.Thanh Xuân, Hà Nội
- Kho Tổng: 938 Quốc Lộ 1A, P.Linh Xuân, TP.HCM
🌼 Shopee: https://shopee.vn/vanlonggroups
🌼 Tiktok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thietbichamsocsuckhoe
🌼 Tiki: https://tiki.vn/cua-hang/cham-soc-suc-khoe-van-long
🌼 Lazada: https://www.lazada.vn/shop/van-long-our-needs-your-business